January 7, 2019
Radiation is something most people have heard of, usually in the context of the dangers it can cause. Many associate radiation with the sun, which can cause minor sunburn or even increase your chances of skin cancer.
However, radiation actually takes many forms, not all of which are dangerous. Among the different types of electromagnetic waves, radiation is a form of energy that can be found all around us. The human body itself emits a form of radiation, which is emitted constantly as ambient heat, also known as body heat.
The Spectrum of Electromagnetic Radiation Is Made of Seven Main Sections
So, what is the electromagnetic spectrum? To understand its role in therapy, let’s consider the seven key sections.
- Radio waves are emitted by radio stations and picked up by a radio.
- Microwave radiation is used in radar technology and is commonly used to cook food in a short amount of time, such as in a microwave.
- Infrared light is emitted by our bodies and other objects as heat but is not visible to the human eye.
- Visible light is light energy that we can see with our eyes, such as a light bulb or a firefly, as well as the stars in the night sky.
- Ultraviolet radiation is given off by the sun and can cause damage to the skin if overexposed to its rays.
- X-rays are used in various devices to see a better picture of the internal structure of an object.
- Gamma rays are used to get a deeper image, similar to x-rays, except it allows for a more precise image to be collected.
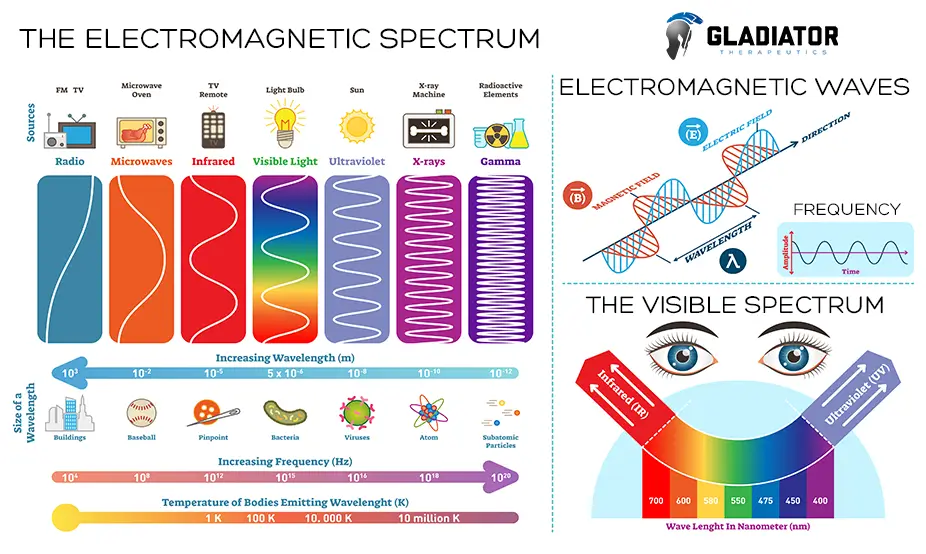
Radiation is broken down into frequency, wavelength, and energy.
- Frequency is measured in cycles per second, or Hertz.
- Wavelength is measured in meters.
- Energy is measured in electron volts.
Now that you know what the electromagnetic spectrum is, you should be able to understand the primary difference between the opposite spectrums of electromagnetic radiation. This is measured by wavelength, frequency, and the amount of energy given off. The wavelength of radiation given off by radio waves is longer, while the wavelength given off by gamma rays is much shorter. The frequency of radiation given off by radio waves is lower, while the frequency given off by gamma rays is much higher. The energy given off by radio waves is lower, while the energy given off by gamma rays is much higher.
When looking at the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, it is important to note that some areas of the spectrum give off radiation in the form of light, also known as photons. These photons, which are a stream of mass-less particles, travel in a wave-like pattern at the speed of light. Photons are not in radio waves or microwaves, but they are found in infrared light through gamma rays.
The various types of electromagnetic waves range from radio waves, which produce the lowest energy and longest wavelength, to gamma rays, which have the highest energy and shortest wavelength. Visible light, which is what the human body can see freely, lies in the middle of the electromagnetic spectrum. Radio waves are made up of the lowest amount of energy, while gamma rays are made up of the highest amount of energy.
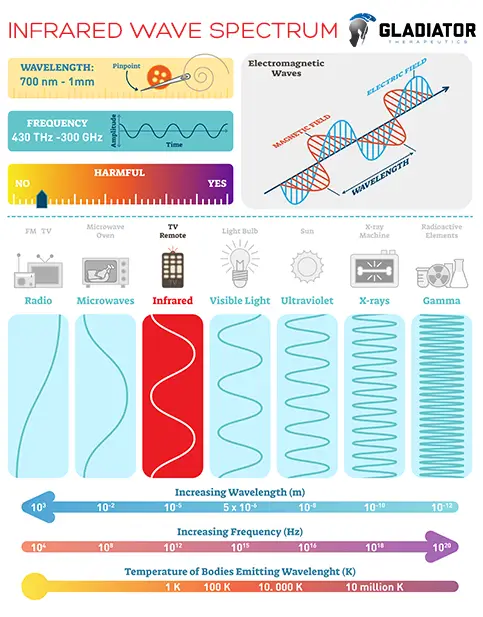
Three Types of Infrared (IR) Radiation
Infrared spans a broad temperature range and exhibits diverse heat characteristics across frequencies. For this reason, it is categorized into three types of electromagnetic waves based on its distinct physical properties:
- Near-infrared radiation (NIR): NIR spans 700nm to 1,300nm (0.7 to 1.3 microns) with a frequency of approximately 215 THz to 400 THz.
- Mid-infrared radiation (MIR): This band spans 1,300 nm to 3,000 nm (1.3 to 3 microns), with frequencies from 20 THz to 215 THz.
- Far infrared radiation (FIR): Akin to microwaves, FIR spans 3,000 nm to 1 mm (3 to 1,000 microns), with frequencies from 0.3 THz to 20 THz.
Among the infrared radiation types, only NIR transfers in the form of heat energy, while FIR transfers in the form of photons, not heat, which is what makes FIR unique, differentiating itself from conventional NIR technology that relies on heat energy. The thermoreceptors within human skin cells read FIR as radiant heat.
Far Infrared vs. Infrared
The term infrared radiation refers to all three types of infrared radiation, while far infrared radiation is a subset form of infrared radiation, which is most commonly used for biological effects.
Far-infrared therapy harnesses far-infrared radiation, a segment of the electromagnetic spectrum. Although invisible to the human eye, infrared light can be felt as heat. “Far” denotes its position on the light spectrum. These light waves can have a warming effect on your body, without heating the surrounding air. They can penetrate the deeper layers of body tissue, making them the preferred choice for therapeutic applications.
Thanks to the advancements in science and technology, it is possible to utilize this radiation as a form of treatment for certain medical conditions and ailments. The radiation is used to stimulate cells and tissues because it is safe and effective for use on human (and animal) cells and tissues. Unlike higher forms of radiation, far infrared photons don’t permanently alter or damage the cells. That is why the therapeutic uses of FIR radiation are becoming more promising in the medical community.
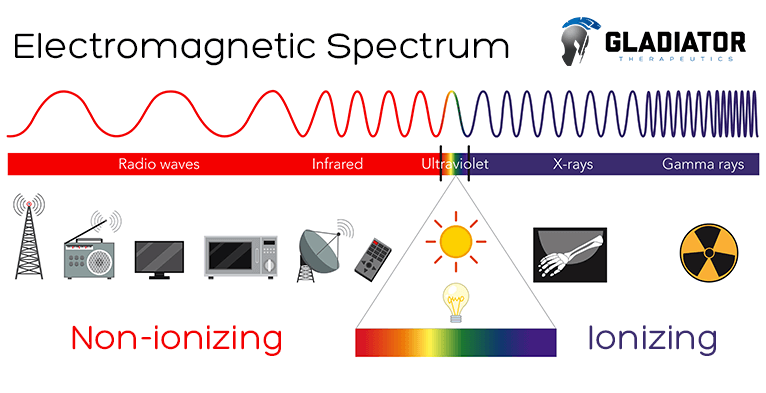
Non-ionizing vs. Ionizing
As mentioned, the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation is made up of different degrees of radiation, and some of that radiation can result in biological changes if overexposed to them.
- Non-ionizing forms of radiation consist of non-thermal, thermal, and some of the optical spectrum within the electromagnetic spectrum.
- The lower the energy is, the less dangerous it becomes to the body.
- For example, radiation within the optical view of the spectrum, like a heat lamp, can be therapeutic. While a tanning bed can also be therapeutic, overexposure can become dangerous.
- With a heat lamp giving off infrared radiation, the human eye can see the energy in the form of light and feel it in the form of heat. The wavelength only penetrates into the topmost layer of the body and excites the electrons. This is referred to as non-ionizing.
- Meanwhile, a tanning bed can offer similar therapeutic benefits, although the energy is higher. This can make it more dangerous and is known as ionizing.
- A tanning bed uses ultraviolet radiation to mimic that of the sun. If overexposed to this form of radiation, the body will become damaged or burned.
- Ultraviolet rays through gamma rays cannot be seen by the human eye, but they can damage DNA and other cells within the body. This end of the electromagnetic spectrum is the most common form of radiation.
- Most of us are taught to fear it as too much sun can damage our cells, resulting in skin cancer.
- Similarly, the higher the amount of radiation from a medical scan (x-ray to PET scan or MRI), the more dangerous it can be for the cells of the body.
Learn More About Gladiator Therapeutics Far Infrared Devices
The Gladiator Therapeutics Far Infrared Devices use far infrared technology through our patented ceramics, which are encased in a hypoallergenic silicone rubber. The Gladiator Devices increase circulation throughout the body by breaking down the water molecule clusters within your blood into smaller molecule clusters, allowing for better blood flow. Better blood flow circulates healthy oxygen and nutrients into the cells and removes the wastes from the cells.
As a prominent research and development firm, we are committed to addressing medical conditions with limited treatment options. For this, we harness the cellular regeneration properties of our patented technology. Our goal is to create non-powered FIR medical devices based on scientific evidence, catering to diverse indications like wound healing and physical recovery from tissue damage or surgical procedures. Contact us today to learn more.

